引言
检索增强生成(RAG)解决方案已无处不在。在过去几年中,随着组织在客户服务、医疗健康、情报分析等领域广泛采用RAG或混合RAG方案,其发展速度令人瞩目。然而,人们应如何有效评估这些解决方案?又有哪些方法可以用来判断RAG模型的优势与不足呢?
本文将通过使用LangChain等工具,利用开源研究数据构建一个聊天机器人,以此作为RAG的入门介绍。同时,还将利用DeepEval对RAG管道的检索器和生成器进行全面评估。最后,将讨论针对RAG解决方案进行人工测试的方法。
检索增强生成 (RAG)
随着大型语言模型(LLM)的兴起,尽管它们经过海量数据集训练,但有时仍会给出不准确的答案,这引发了广泛的批评。为解决这一问题,检索增强生成(RAG)应运而生。它结合了搜索和生成能力,在生成响应之前会参考特定上下文信息。
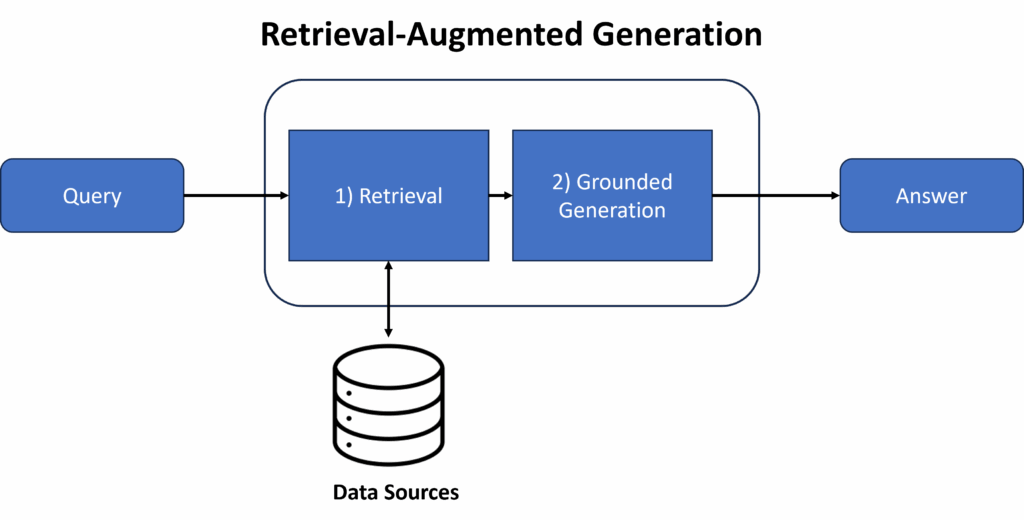
图片来源:作者
过去几年,RAG因其能有效减少幻觉并提升事实准确性而广受欢迎。它具有灵活性高、易于更新且成本远低于微调LLM等优势。如今,人们日常生活中经常接触到RAG解决方案。例如,许多企业已利用RAG构建内部聊天机器人,帮助员工查询知识库,也开发了外部聊天机器人来支持客户服务及其他业务职能。
构建RAG管道
在构建RAG解决方案时,文章将使用与人工智能相关的开源研究摘要数据。这些数据可用于在提问人工智能、机器学习等问题时生成更具“技术性”的答案。
所用数据来源于OpenAlex API (https://openalex.org/),这是一个全球性的开源研究数据集/目录,数据在CC0许可下可免费访问。
数据摄取
首先,需要使用OpenAlex API加载数据。以下代码展示了如何根据出版年份和关键词进行搜索。通过使用“深度学习”、“自然语言处理”、“计算机视觉”等关键词,搜索与AI/ML相关的研究。
import pandas as pd
import requests
def import_data(pages, start_year, end_year, search_terms):
"""
This function is used to use the OpenAlex API, conduct a search on works, a return a dataframe with associated works.
Inputs:
- pages: int, number of pages to loop through
- search_terms: str, keywords to search for (must be formatted according to OpenAlex standards)
- start_year and end_year: int, years to set as a range for filtering works
"""
#create an empty dataframe
search_results = pd.DataFrame()
for page in range(1, pages):
#use paramters to conduct request and format to a dataframe
response = requests.get(f'https://api.openalex.org/works?page={page}&per-page=200&filter=publication_year:{start_year}-{end_year},type:article&search={search_terms}')
data = pd.DataFrame(response.json()['results'])
#append to empty dataframe
search_results = pd.concat([search_results, data])
#subset to relevant features
search_results = search_results[["id", "title", "display_name", "publication_year", "publication_date",
"type", "countries_distinct_count","institutions_distinct_count",
"has_fulltext", "cited_by_count", "keywords", "referenced_works_count", "abstract_inverted_index"]]
return(search_results)
#search for AI-related research
ai_search = import_data(30, 2018, 2025, "'artificial intelligence' OR 'deep learn' OR 'neural net' OR 'natural language processing' OR 'machine learn' OR 'large language models' OR 'small language models'")
查询OpenAlex数据库时,摘要以倒排索引的形式返回。以下是一个函数,用于还原倒排索引并返回摘要的原始文本。
def undo_inverted_index(inverted_index):
"""
The purpose of the function is to 'undo' and inverted index. It inputs an inverted index and
returns the original string.
"""
#create empty lists to store uninverted index
word_index = []
words_unindexed = []
#loop through index and return key-value pairs
for k,v in inverted_index.items():
for index in v: word_index.append([k,index])
#sort by the index
word_index = sorted(word_index, key = lambda x : x[1])
#join only the values and flatten
for pair in word_index:
words_unindexed.append(pair[0])
words_unindexed = ' '.join(words_unindexed)
return(words_unindexed)
#create 'original_abstract' feature
ai_search['original_abstract'] = list(map(undo_inverted_index, ai_search['abstract_inverted_index']))
创建向量数据库
接下来,需要生成嵌入向量来表示这些摘要,并将其存储在向量数据库中。最佳实践是利用向量数据库,因为它们专为低延迟查询而设计,可扩展处理数十亿个数据点。它们还使用专门的索引和最近邻算法,根据上下文和/或语义相似性快速检索数据,这对于LLM应用至关重要。
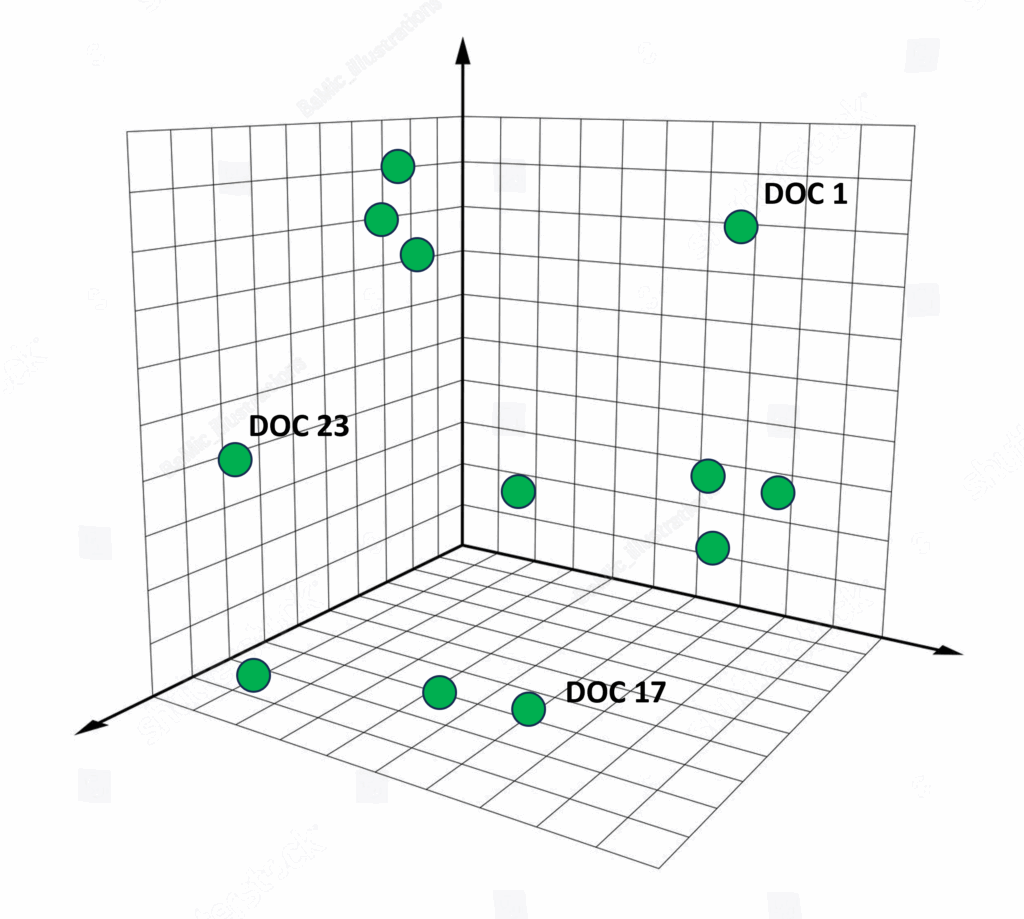
图片来源:作者
首先,从LangChain导入必要的库,并从HuggingFace加载嵌入模型。尽管使用更大的嵌入模型可能会获得更好的结果,但这里选择了一个较小的模型,以强调管道的速度。
可以通过Hugging Face的MTEB排行榜 (https://huggingface.co/spaces/mteb/leaderboard) 查找并比较不同嵌入模型的大小、性能和预期用途等。
from langchain_community.docstore.in_memory import InMemoryDocstore
from langchain_community.vectorstores import FAISS
from langchain_huggingface.embeddings import HuggingFaceEmbeddings
from langchain_core.documents import Document
#load embedding model
embeddings = HuggingFaceEmbeddings(model_name="thenlper/gte-small")
接下来,使用FAISS(或LangChain对FAISS的封装)创建向量数据库。首先创建索引,并格式化数据和文档,同时存储它们的元数据(标题和年份)。然后创建一个ID列表,将文档和ID添加到数据库中,并将数据库保存在本地。
#save index with faiss
index = faiss.IndexFlatL2(len(embeddings.embed_query("hello world")))
#format abstracts as documents
documents = [Document(page_content=ai_search['original_abstract'][i], metadata={"title": ai_search['title'][i], "year": ai_search['publication_year'][i]}) for i in range(len(ai_search))]
#create list of ids as strings
n = len(ai_search)
ids = list(range(1, n + 1))
ids = [str(x) for x in my_list]
#add documents to vector store
vector_store.add_documents(documents=documents, ids=ids)
#save the vector store
vector_store.save_local("Data/faiss_index")
借助LangChain的向量存储,可以直接查询文档。可以通过搜索“计算机视觉”来快速测试其功能。从下方返回的第一个文档“Face Detection and Recognition Using OPENCV”可以看出,它与计算机视觉高度相关。
#test that vector database is working
vector_store.similarity_search("computer vision", k=3)
[Document(id='783', metadata={'title': 'FACE DETECTION AND RECOGNITION USING OPENCV', 'year': 2020}, page_content='Computer Vision is one of the most fascinating and challenging tasks in the field of Artificial Intelligence.Computer Vision serves as a link between computer software and the visuals we see around us.It enables...
创建RAG管道
接下来,开发RAG管道。RAG解决方案的一个主要组成部分是用于生成响应的生成模型。为此,将使用LangChain中的OpenAI模型。
为了比较在实现RAG管道前后的响应,可以向“基础”模型提问:“计算机视觉领域最新的进展是什么?”
from langchain_openai import OpenAI
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQA
from langchain import PromptTemplate
#set API key
OPENAI_API_KEY = os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY","API KEY")
#load llm
llm = OpenAI(openai_api_key=OPENAI_API_KEY)
#test llm response
llm.invoke("What are the most recent advancements in computer vision?")
‘
1. Deep Learning: Deep learning, a subset of machine learning, has shown significant progress in computer vision tasks such as object detection, recognition, and image classification. It uses neural networks with multiple hidden layers to learn and extract features from images, leading to more accurate and efficient results.
2. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): GANs are a type of deep learning algorithm that generates new images by learning from a large dataset. They have been used in tasks such as image synthesis, super-resolution, and image-to-image translation, and have shown impressive results in creating realistic images.
3. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): CNNs are a type of deep learning algorithm that has revolutionized the field of computer vision. They are highly effective in extracting features from images and have been used in various tasks such as image classification, object detection, and segmentation.
4. Transfer Learning: Transfer learning allows a pre-trained model to be used on a different task or dataset without starting from scratch. It has shown promising results in computer vision tasks, especially for tasks with limited training data.
5. Image Segmentation: With advancements in deep learning, image segmentation has become more accurate and efficient. It involves dividing an image into different regions or segments to identify objects’
从上述响应可以看出,它提供了计算机视觉的总体概述、其工作原理的高级描述以及不同类型的模型和应用。尽管这是一个很好的总结,但它并未直接回答具体问题。这正是RAG大显身手的机会!
接下来,构建RAG管道的各个组件。首先,需要一个检索器来获取与查询最相关的k个文档。然后构建一个提示,指导模型如何回答问题。最后,将它们与基础生成模型结合,创建完整的管道。
重新测试查询“计算机视觉领域最新的进展是什么?”
#test that vector database is working
retriever = db.as_retriever(search_kwargs={"k": 3})
#create a prompt template
template = """<|user|>
Relevant information:
{context}
Provide a concise answer to the following question using relevant information provided above:
{question}
If the information above does not answer the question, say that you do not know. Keep answers to 3 sentences or shorter.<|end|>
<|assistant|>"""
#define prompt template
prompt = PromptTemplate(
template=template,
input_variables=["context", "question"])
#create RAG pipeline
rag = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(llm=llm, chain_type="stuff", retriever=retriever, return_source_documents=True,
chain_type_kwargs={"prompt": prompt}, verbose = True)
#test rag response
rag.invoke("What are the most recent advancements in computer vision?")
The most recent advancements in computer vision include the emergence of large language models equipped with vision capabilities, such as OpenAI’s GPT-4V, Google’s Bard AI, and Microsoft’s Bing AI. These models are able to analyze images and have the ability to access real-time information, making them directly embedded in many applications. Further advancements are expected as AI continues to rapidly evolve.
这个响应更好地回答了问题。它直接指出了最新的进展,提到了具体的模型能力以及它们如何推动计算机视觉的发展。这对于构建技术型聊天机器人来说是一个充满希望的结果。
但这并非一次全面的评估。接下来,将针对多项指标进一步测试RAG解决方案,以判断其是否已准备好投入生产。
以LLM作为评估法官
为了开始评估RAG解决方案,将使用另一个生成模型来判断RAG解决方案如何满足特定标准。尽管“以LLM作为评估法官”的方法存在一些局限性且需要谨慎使用,但它们提供了极大的灵活性和效率。此外,它们还能在评估过程中提供详细的见解,正如后续内容所示。
RAG由两个主要组件组成:检索器和生成器。将对这些组件进行独立评估。评估结果可能会促使调整超参数、更换嵌入模型或使用不同的生成模型。
检索器评估
首先,评估检索器,即负责获取相关内容的组件。将从以下三个指标进行判断:
- 上下文精确度 (Contextual Precision): 代表检索系统正确排序相关节点的能力。它首先使用LLM判断每个节点是否与输入相关,然后计算加权累积精确度。
- 上下文召回率 (Contextual Recall): 代表检索系统从知识库中所有可用相关信息中捕获所有相关信息的能力。
- 上下文相关性 (Contextual Relevancy): 评估为给定输出呈现的信息的总体相关性。
首先,导入库并初始化指标。
from deepeval import evaluate
from deepeval.test_case import LLMTestCase, LLMTestCaseParams
from deepeval.metrics import (
ContextualPrecisionMetric,
ContextualRecallMetric,
ContextualRelevancyMetric)
#set your OpenAI API key
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "API KEY"
# Initialize metrics
contextual_precision = ContextualPrecisionMetric()
contextual_recall = ContextualRecallMetric()
contextual_relevancy = ContextualRelevancyMetric()
接下来,需要构建一个测试用例,即给定查询的预期输出。这些测试数据集的构建可能很困难,需要领域专家的参与,他们了解可能提出的问题以及这些问题的预期答案。
在此示例中,将仅创建一个带有模拟预期输出的测试用例。这不会给出真实结果,但会提供一个示例结果。
#define user query
input = 'What are the most recent advancements in computer vision?'
#RAG output
actual_output = rag.invoke(input)['result']
#contexts used from the retriver
retrieved_contexts = []
for el in range(0,3):
retrieved_contexts.append(rag.invoke(input)['source_documents'][el].page_content)
#expected output (example)
expected_output = 'Recent advancements in computer vision include Vision-Language Models (VLMs) that merge vision and language, Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) for 3D scene generation, and powerful Diffusion Models and Generative AI for creating realistic visuals. Other key areas are Edge AI for real-time processing, enhanced 3D vision techniques like NeRFs and Visual SLAM, advanced self-supervised learning methods, deepfake detection systems, and increased focus on Ethical AI and Explainable AI (XAI) to ensure fairness and transparency.'
结合上述组件,现在可以构建测试用例并计算三个指标。
#create test case
test_case = LLMTestCase(
input=input,
actual_output=actual_output,
retrieval_context=retrieved_contexts,
expected_output=expected_output)
#compute contextual precision and print results
contextual_precision.measure(test_case)
print("Score: ", contextual_precision.score)
print("Reason: ", contextual_precision.reason)
#compute contextual recall and print results
contextual_recall.measure(test_case)
print("Score: ", contextual_recall.score)
print("Reason: ", contextual_recall.reason)
#compute relevancy precision and print results
contextual_relevancy.measure(test_case)
print("Score: ", contextual_relevancy.score)
print("Reason: ", contextual_relevancy.reason)
Score: 1.0 Reason: The score is 1.00 because the relevant nodes are ranked at the top: the first node discusses ‘recent progress on computer vision algorithms’ and ‘prominent achievements,’ and the second node covers the ‘evolution of computer vision’ and foundational advancements. The irrelevant node, which only describes the OpenCV toolkit and lacks discussion of recent advancements, is correctly ranked last. This perfect ordering ensures the highest contextual precision.
Score: 0.0 Reason: The score is 0.00 because none of the sentences in the expected output can be traced back to any node(s) in the retrieval context; there is no overlap or relevant information present.
Score: 0.5555555555555556 Reason: The score is 0.56 because, while there are several statements that discuss recent progress and deep learning advancements in computer vision (e.g., ‘The prominent achievements in computer vision tasks such as image classification, object detection and image segmentation brought by deep learning techniques are highlighted.’), much of the context is general background or unrelated details (e.g., ‘The explanation of the term ‘convolutional’ as a mathematical operation is not directly relevant to the advancements in computer vision.’).
如上所示,使用LLM作为法官的好处之一是能够获得关于分数详细的反馈。例如,上下文相关性得到55%的分数,是因为LLM认为某些信息不必要(稍稍偏离了关于CNNs的讨论)。
还可以使用DeepEval的“evaluate”函数更好地自动化此过程。这在测试RAG的多个测试用例时非常有用。
#run all metrics with 'evaluate' function
evaluate(test_cases=[test_case],
metrics=[contextual_precision, contextual_recall, contextual_relevancy])
生成器评估
接下来,评估生成器,它根据检索器提供的上下文生成响应。这里将计算两个指标:
- 答案相关性 (Answer Relevancy): 类似于上下文相关性,评估生成器中的提示模板是否能够指导LLM根据上下文给出相关的输出。
- 忠实度 (Faithfulness): 评估生成器中使用的LLM是否能够输出不产生幻觉或不与检索上下文中呈现的任何事实信息相矛盾的信息。
和之前一样,初始化这些指标。
from deepeval.metrics import AnswerRelevancyMetric, FaithfulnessMetric
answer_relevancy = AnswerRelevancyMetric()
faithfulness = FaithfulnessMetric()
#compute answer relevancy and print results
answer_relevancy.measure(test_case)
print("Score: ", answer_relevancy.score)
print("Reason: ", answer_relevancy.reason)
#compute faithfulness and print results
faithfulness.measure(test_case)
print("Score: ", faithfulness.score)
print("Reason: ", faithfulness.reason)
Score: 1.0 Reason: The score is 1.00 because the answer was fully relevant and addressed the question directly without any irrelevant information. Great job staying focused and informative!
Score: 1.0 Reason: Great job! There are no contradictions, so the actual output is fully faithful to the retrieval context.
如上所示,生成器运行得非常好(在当前测试用例下)。答案保持相关性,模型也没有自相矛盾。同样,可以使用“evaluate”函数来评估多个测试用例。
#run all metrics with 'evaluate' function
evaluate(test_cases=[test_case],
metrics=[answer_relevancy, faithfulness])
使用这些指标的一个注意事项是它们是通用性的,只关注生成输出的几个方面,例如相关性。但也可以创建定制的指标来确定RAG解决方案在特定重要领域中的表现。
例如,可以提出诸如“RAG如何处理黑色幽默?”或“输出是否以儿童友好的水平编写?”之类的问题。在此示例中,将确定RAG提供技术性书面响应的能力。
from deepeval.metrics import GEval
#create evaluation for technical language
tech_eval = GEval(
name="Technical Language",
criteria="Determine how technically written the actual output is",
evaluation_params=[LLMTestCaseParams.ACTUAL_OUTPUT])
#run evaluation
tech_eval.measure(test_case)
print("Score: ", tech_eval.score)
print("Reason: ", tech_eval.reason)
Score: 0.6437823499114202 Reason: The response uses appropriate technical terminology such as ‘deep learning’, ‘image classification’, ‘object detection’, ‘image segmentation’, ‘GPUs’, and ‘FPGAs’. The explanations are clear but somewhat general, lacking specific examples or recent breakthroughs. The technical detail is moderate, mentioning both algorithmic and hardware aspects, but does not delve into particular models or methods. The writing is mostly formal and adheres to technical conventions, but the depth and specificity could be improved.
在上面的输出中,可以看出RAG生成了具有一定技术性的答案。它使用了适当的技术术语并给出了清晰的解释,但缺乏具体示例。这可能是由于使用摘要作为数据源,而摘要的写作水平通常较高。
人工评估
尽管“以LLM作为评估法官”的方法提供了大量有用的信息,但它们是通用性的,并且应谨慎对待,因为它们无法完全评估真实世界的适用性。然而,人类能够更好地探索这一点,因为没有人比组织内的领域专家更了解数据。
人工评估通常审查正确性、论证质量和流畅性。评估人员必须确定输出是否准确、是否将检索到的证据与结论进行逻辑连接、是否自然且有用。重要的是要牢记RAG解决方案的数据、用户和目的,以正确满足这些特定领域的要求。
总结
在本文中,通过利用FAISS、LangChain等工具,使用开源研究数据成功构建了一个RAG管道。还深入探讨了如何评估RAG解决方案,对检索器和生成器都进行了评估。DeepEval等库利用“以LLM作为评估法官”的指标来构建测试用例,并确定相关性、忠实度等。最后,讨论了人工评估在确定RAG解决方案真实世界适用性方面的重要性。