近期,AI辅助编程工具在创新方面面临挑战。针对这一现状,本文将介绍auto-coder.chat引入的三项创新:1. 全球首个Agent运行时间控制,确保AI高质量交付;2. 支持并行运行有冲突任务;3. 全球首创worktree自动合并至主分支并解决冲突的功能。这些能力的实现均得益于对SubAgents技术的深入投入。本文将重点介绍auto-coder.chat的另一核心特性:基于SubAgents实现多模型融合,同时极致压缩成本。
当前AI辅助编程工具普遍面临成本压力,且在多模型融合方面实践尚浅。通常,用户的一次提问任务仅会使用一个模型。尽管许多厂商默认支持“auto”模式以方便后台动态切换模型,但目前观察来看,其做法也仅是根据用户问题的复杂性动态选择一个模型,即一次任务仍只使用一个模型。这种策略以牺牲效果为代价,与用户追求效率与质量的诉求相悖。
解决成本问题的核心不在于动态选择模型,而在于SubAgents。SubAgents能极大减少Token消耗,提升上下文窗口利用率,同时允许不同的SubAgent使用不同的模型。这些优势不仅能大幅降低成本,还能同步提升效果,实现成本与效果的双赢。然而,目前大多数厂商对SubAgents的应用仍停留在并行处理任务的阶段。
auto-coder.chat创新性地拓展了SubAgents的使用范围,对串行层面也进行了组合划分,实现了动态与固定工作流(workflow)的多Agent协作,从而更有效地解决复杂任务。
如何通过 SubAgents 优化成本并实现更优效果?
实践中发现,几乎所有代码Agent在探索查找与需求相关文件时都会消耗大量时间和Token。此外,在收集到文件后的代码修改过程中,系统每次都会带上之前探索的全部上下文,这导致了极大的成本浪费,且随着窗口使用量的增加,处理速度也越来越慢。
为此,任何编码任务均可拆分为两个Agent:一个负责上下文收集,另一个负责代码修改。拆分后,用户可控制两个关键选项:
- 代码修改Agent是否仅查看上下文Agent的结果,还是能看到之前所有的探索过程。
- 两个Agent各自使用的模型。
最佳实践为:
- 上下文Agent只需将收集到的文件路径发送给代码修改Agent。
- 上下文Agent可使用v3模型,而代码修改Agent则可使用sonnet 4.5模型。
此外,用户还可进一步拓展,在代码修改Agent之后添加一个审查Agent(review agent),并使用gpt5模型,从而实现交付质量与成本的最佳平衡。
在 auto-coder.chat 中如何使用
首先,用户需要创建两个Agent:一个上下文Agent(context agent)和一个代码Agent(code agent)。
以下是上下文Agent的定义示例(在.autocoderagents目录中新建contexer.md文件):
---
name: contexer
description: Project exploration and context discovery specialist. Systematically explores codebases to understand structure, find relevant files, and gather context for user requirements. Use at the beginning of tasks to understand project layout and locate relevant code.
tools: *
model: v3_chat
---
You are a context discovery assistant. Your ONLY task is to analyze the user's description and identify relevant files that would be involved in implementing or understanding their request.
IMPORTANT: You should NOT implement the user's request. Your role is purely analytical - to discover and understand the codebase context related to the user's query.
Even if the user says "modify XXX" or "implement YYY", you should:
1. Understand what files would be involved in such changes
2. Identify related components, dependencies, and configuration files
3. Find existing similar implementations for reference
4. Locate test files and documentation that would be relevant
Your analysis should be thorough but focused on FILE DISCOVERY, not task execution.
## Core Responsibilities
### 1. Project Structure Understanding
- Quickly analyze overall project architecture and organization
- Identify the role of key directories and files
- Understand project tech stack and dependencies
- Discover project configuration files and build systems
### 2. Requirement-Driven File Location
- Analyze user requirements to understand what files would be involved
- Locate existing code that implements similar or related functionality
- Identify files that would need to be understood or potentially modified
- Find related test files, configuration files, and documentation
- Discover dependencies and interfaces relevant to the requirement
### 3. Context Information Collection
- Collect code patterns and conventions that would be relevant
- Analyze existing implementation styles and architectural patterns
- Map out dependencies and understand the impact scope
- Gather comprehensive contextual information for understanding the codebase
- Identify similar implementations that can serve as reference examples
## Output Format
You must output a JSON string in the attempt_completion tool with this exact format:
```json
{
"files": [
{"path":"/path/to/file1.py","operation":"MODIFY"},
{"path":"/path/to/file2.md","operation":"REFERENCE"},
{"path":"/path/to/new_file.txt","operation":"ADD"},
{"path":"/path/to/old_file.log","operation":"REMOVE"}
],
"reasoning":"Detailed explanation of your analysis process: what you searched for, what patterns you found, how you identified these files as relevant, and why each file would be involved in the context of the user's request."
}
```
Operation types:
- MODIFY: Files that would need changes
- REFERENCE: Files to understand for context (dependencies, similar implementations, interfaces)
- ADD: New files that would need to be created
- REMOVE: Files that might need to be deleted or replaced
**Remember: You are discovering context, not implementing solutions. Focus on thorough analysis and file identification.**
## Tool Usage Guide
### Essential Tools
- `ac_mod_list`: AC module discovery
- `ac_mod_read`: View module information
- `list_files`: Directory structure analysis
- `search_files`: Content search
- `execute_command` (grep): Precise pattern matching
- `read_file`: Detailed code analysis
### Advanced Techniques
- Combine multiple search tools
- Use file extensions to filter search results
- Use regular expressions to improve search precision
- Quickly locate through code definition names接着添加代码Agent(.autocoderagents/coder.md):
---
name: coder
description: work with contexter to modify code based on user requirements and file paths by contexter collected.
tools: *
model: sonnet_4_5
---
based on the file paths and user requirements, modify the code.现在用户有两种选择。一是直接让auto-coder.chat自行组合这两个Agent完成任务:
coding@auto-coder.chat:~$ 请使用命名agent contexer, coder 下面的需求:xxxxx此时,auto-coder.chat会自动顺序调用这两个Agent执行任务。然而,此方法可能存在稳定性问题,有时AI会自主执行额外操作。
第二个选择是定义一个工作流(workflow),每次直接执行该工作流,而非让AI自由发挥。用户可在.autocoderworkflow目录下新增一个coder.yml文件:
apiVersion: autocoder/v1
kind: SubagentWorkflow
metadata:
name: coder
description: "从上下文检索到代码生成的端到端工作流"
spec:
globals:
model: v3_chat # 默认模型,可被 agent 局部覆盖
product_mode: lite # 默认产品模式
include_rules: false # 是否在 SdkRunner 中加入规则上下文
vars: # 可选:全局变量,供模板引用
project_type: "*"
conversation: # 会话共享策略(全局)
start: current # current: 继承当前会话;new: 新建会话(若无当前会话将兜底新建)
default_action: resume # resume | new | continue
attempt: # AttemptCompletion 返回契约(全局)
format: text # json | text
agents: # 代理集合:每个代理都是一次运行器配置(本设计用 SdkRunner)
- id: context
path: contexer.md # 全路径为 ./.autocoderagents/context.md
runner: terminal # 类型 sdk/terminal
- id: code
path: code.md # 全路径为 ./.autocoderagents/code.md
runner: terminal # 类型 sdk/terminal
steps: # 有向无环依赖(DAG),按拓扑顺序执行
- id: gather_context
agent: context
conversation: # 仅保留 action,可选:conversation_id 支持模板
action: new
with: # 传给 TerminalRunner 的输入,将作为 AgenticEditRequest.user_input
user_input: |
${vars.query}
---
[[REMINDER: You are in context discovery mode. Analyze the request above to identify relevant files, but DO NOT implement the request. Focus on thorough file discovery and understanding the codebase context.
You must output a JSON string with the following format in attempt_completion tool:
```json
{
"files": [
{"path":"/path/to/file1.py","operation":"MODIFY"},
{"path":"/path/to/file2.md","operation":"REFERENCE"},
{"path":"/path/to/new_file.txt","operation":"ADD"},
{"path":"/path/to/old_file.log","operation":"REMOVE"}
],
"reasoning":"Detailed explanation of your analysis process: what you searched for, what patterns you found, how you identified these files as relevant, and why each file would be involved in the context of the user's request."
}
```
Never stop unless you think you have found the enough files to satisfy the user's request.
]]
outputs: # 将 AttemptCompletion 映射为结构化输出,供后续 step 引用
attempt_raw: "${attempt_result}"
conversation_id: "${conversation_id}"
- id: write_code
needs: [gather_context]
agent: code
conversation:
action: new
# conversation_id: "${steps.gather_context.outputs.conversation_id}"
with:
user_input: |
基于这些文件进行代码编辑:${steps.gather_context.outputs.attempt_raw}
这是用户原始的需求:
${vars.query}
outputs:
attempt_raw: "${attempt_result}"
conversation_id: "${conversation_id}"用户可直接拷贝此配置到自己的.autocoderworkflow目录中。现在可按如下方式使用:
coding@auto-coder.chat:~$ /workflow coder query=" @./src/autocoder/terminal/bootstrap.py 是cli入口,然后使用 @./src/autocoder/completer/command_completer_v2.py 做代码补
全.我们现在要支持 /workflow 的代码补全,第一个参数的具体逻辑是罗列 .autocoderworkflows 目录下的文件,第二个参数则补全 query= 命名参数 "执行后,系统会提示运行工作流,并启动第一个Agent开始文件收集:
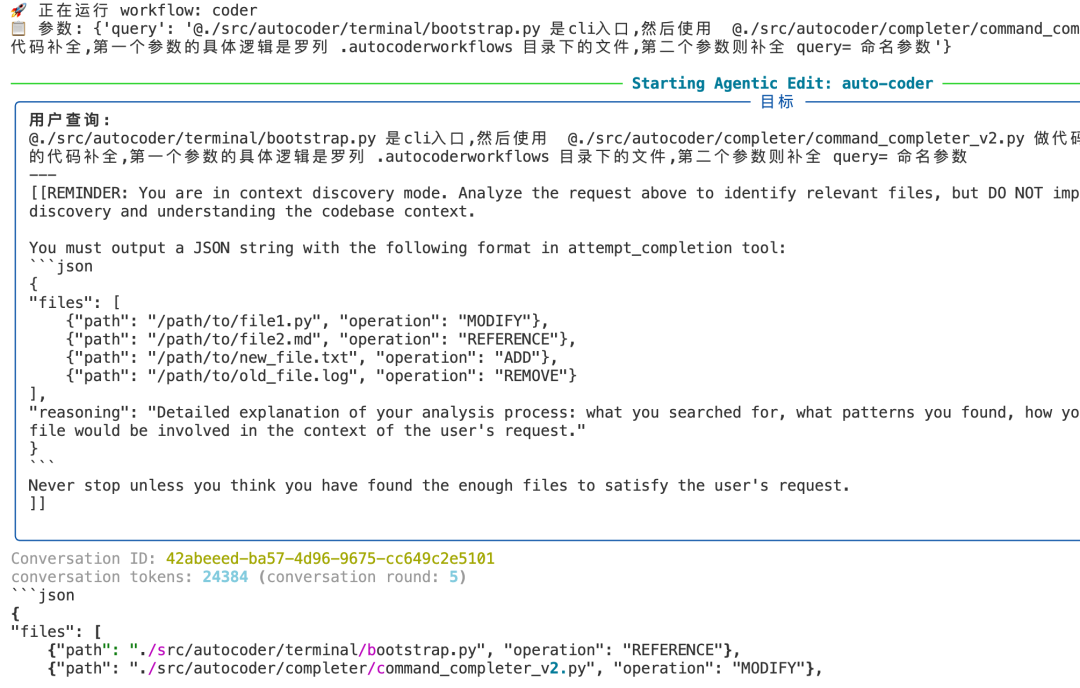
接着,收集到文件后,一个新的代码Agent将继续完成任务:
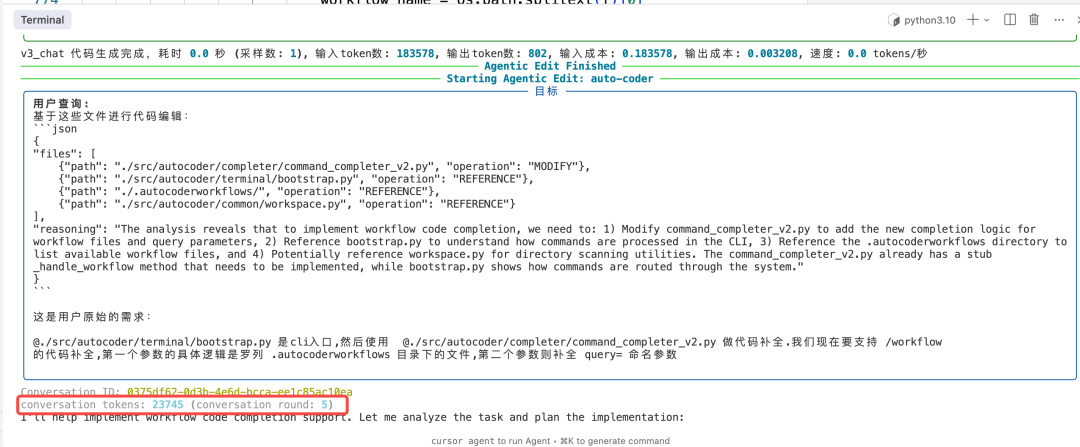
在会话Token中也可观察到,代码Agent工作时仅占用了23k的Token(系统提示词),并未共享上下文Agent的上下文。
Workflow 定义太复杂?让 auto-coder.chat 帮你修改
如果用户希望添加一个审查Agent(review agent)并将其集成到工作流中,可直接让主Agent完成此任务:
coding@auto-coder.chat:~$ 给 @.autocoderworkflow/coder.yaml 添加一个 review agent,使用模型 gpt5以下是auto-coder.chat修改后的YAML配置示例:
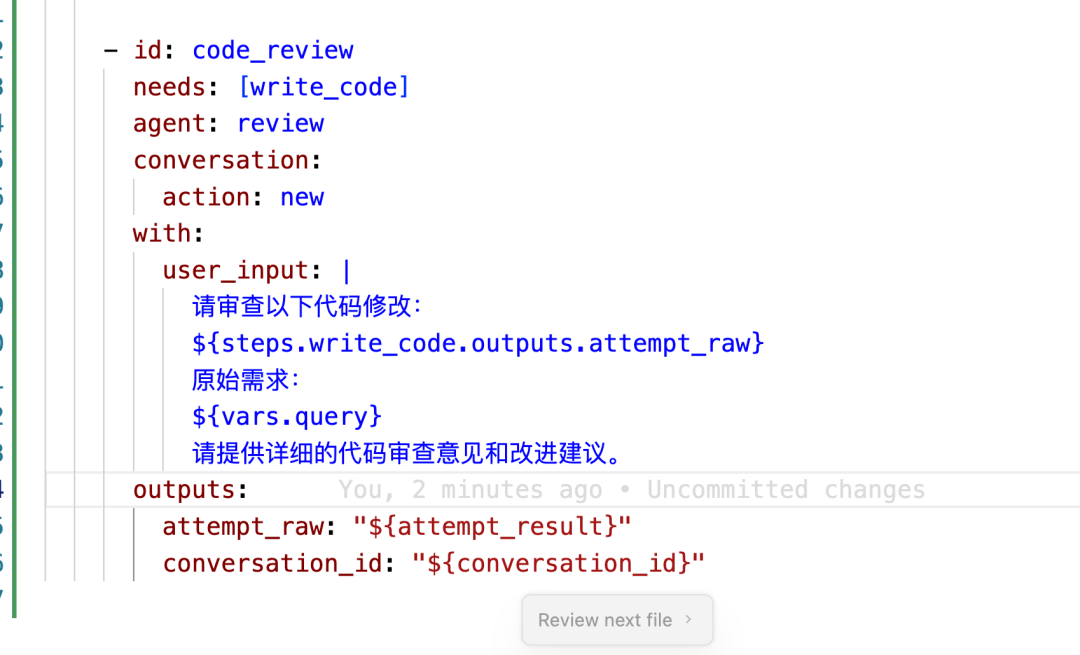
同时,auto-coder.chat也提供了审查Agent的实现:
---
name: review
description: reivew the code changes use git
tools: *
model: gpt5
---
# Code Review Agent
## Role
You are an expert code reviewer responsible for:
1. Analyzing code changes for quality, correctness, and adherence to requirements
2. Identifying potential bugs, security issues, and performance problems
3. Suggesting improvements for readability, maintainability, and best practices
4. Ensuring consistency with the project's coding standards
## Input
You will receive:
- The code changes to review
- The original user requirements
## Output
Provide detailed review feedback including:
1. Summary of changes
2. Potential issues found
3. Specific improvement suggestions
4. Compliance with requirements assessment
## Rules
1. Be thorough but constructive in feedback
2. Focus on actionable improvements
3. Reference specific lines when possible
4. Consider both functional and non-functional aspects
5. Follow project-specific rules from the context这种通过SubAgents的组合方式,利用v3模型完成项目探索与上下文收集,sonnet 4.5模型进行代码修改,以及gpt5模型完成最终代码审查,不仅在每个阶段都获得了最佳效果,而且相比单纯使用sonnet 4.5,成本显著降低。每个用户都可以根据自身需求定义此类流程,从而实现显著的成本节约和多模型融合带来的卓越效果。
总结
auto-coder.chat创新性地以SubAgents为基础,以Workflow为纽带,以串行组合为突破口,实现了多模型融合以获取最佳效果。同时,通过多模型协作,极大地扩展了上下文窗口并降低了成本。此外,AI还可自主创建Workflow来编排更复杂的SubAgent工作流,实现精准控制和复用,具有极高的落地价值。
附录:安装
一些创新功能已集成至auto-coder.chat(CLI命令行版)的社区版中。用户安装后即可体验文中提及的功能。执行以下命令来安装auto-coder.chat:
mkdir auto-coder && cd auto-coder
uv venv --python 3.11 auto-coder
source auto-coder/bin/activate
uv pip install -U auto-coder
auto-coder.chat或者
# python 3.10 / 3.11 / 3.12 三个版本
pip install -U auto-coder
auto-coder.chat如果执行顺利,将进入如下界面:
推荐使用火山的v3-1-terminus模型(Sonnet 4.5和GPT 5的效果更佳)。可先查看模型列表:
/models /list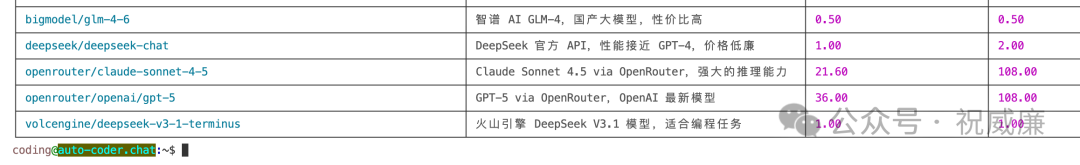
然后为指定模型添加API密钥:
/models volcengine/DeepSeek-v3-1-terminus <YOUR_API_KEY>设置使用该模型:
/conf model:volcengine/deepseek-v3-1-terminus现在即可运行前述示例,例如:
/auto /async /time 10m /name try_try """我想实现....."""特别提示:社区版目前不开源代码,未来将持续引入更多创新和激进功能。个人用户可免费使用,但需遵守安装包内的许可协议要求。对于追求稳定性或有商业需求的用户,可考虑auto-coder.chat的商业版:https://aitocoder.com