如何使用知识图谱和LLM构建智能问答系统
本文将介绍如何基于知识图谱(Knowledge Graph, KG)和大型语言模型(LLM,具体采用Gemma3–4b-it-qat)构建一个简易的问答(QA)系统。选择Gemma3–4b的原因在于其轻量级特性,使其能够在普通笔记本上运行,同时擅长遵循指令。若需了解更多关于知识图谱、Gemma3或本地运行LLM的背景信息,建议查阅相关前置文章。
本指南将以假想智能手机的FAQ文本为例,利用现有代码为其生成知识图谱,并在此基础上搭建一个能回答产品相关问题的系统,例如:
本文将探讨以下内容:
- 什么是问答系统(QA System)
- 系统设计思路
- 代码实现细节
- 系统局限性与未来改进方向
什么是问答系统(QA System)
根据Google的定义:
A question answering (QA) system is a software application that takes a user’s question in natural language and provides a direct, relevant answer by processing the question’s intent and retrieving information from a knowledge source or generating a new response.
在此系统中,知识源将是使用Gemma3生成的一段模拟FAQ文本,可在本博客的Github仓库中获取。通过运行仓库的main.py脚本,可以构建知识图谱并将其保存到输出目录:
python main.py --inputpath ./input/sample-faq.txt --outlabel faq
此命令会将networkx图保存为“nx_graph.pkl”文件,后续在构建问答系统时会进行加载。
系统设计思路
核心思路是从用户问题中提取实体(entities)和关键词(keywords),查找与它们相关的所有节点(nodes)和边(edges),然后将这些信息连同问题一同提供给LLM,使其基于知识图谱中的信息生成答案。具体方案如下:
- 使用LLM从用户问题 q 中抽取命名实体(entity_keywords)和关系/谓词(relation_keywords)。
- 枚举 entity_keywords 中的所有可能配对组合,以便全面查询图,因为无法预设某个实体是源节点还是目标节点。
- 对于第2步得到的每一对 (u, v),在知识图谱G中查找 u 与 v 之间的所有路径,从而发现两个实体之间的所有关系、路径或知识。这一步是关键性的突破。
- 对于找到的每条路径(源节点与目标节点),提取它们之间的关系。例如 (box, include, charger)。
- 将形成的三元组(triple)加入 relations 列表。
- 对 relation_keywords 进行类似处理。对于每个关系 r,找到所有由 r 连接的边,形成三元组并加入同一 relations 列表。
- 最后一步,将这些三元组和问题 q (封装在prompt中)传递给LLM,让其基于给定事实(三元组)和查询生成答案。
代码实现
首先,通过main.py构建知识图谱:
python main.py --inputpath ./input/sample-faq.txt --outlabel faq
接着从上一步生成的pickle文件中加载图:
import pickleG = pickle.load(open(graph_file, "rb"))
需要定义一个函数,用于接收文本输入和系统级提示(system level prompt),并从LLM获取响应。以下可复用函数实现了该功能:
def get_llm_response(text, system_prompt): response = Ollama.chat(model=model, messages=[ {"role": "system", "content": system_prompt}, {"role": "user", "content": text} ]) resp_content = response['message']['content'] return resp_content
随后,需从给定查询中抽取实体和关系(对应上文的第1步)。一个基础的系统提示词(system prompt)示例如下:
system_prompt_key_words = """You are a helpful assistant, expert of English language who can extracts keyword from the given question in root form (e.g. ran becomes run) and lowercase.The returned keywords should be critical to answer the question.Categorize the keywords into entity and relation keywords.keywords must be in root form and lowercase.The response should be in following format, no additional text:{"entity": [list of entity keywords], "relation": [list of relation keywords]}"""response = get_llm_response(query, system_prompt_key_words)keyword_resp = json.loads(response)entity_keywords = keyword_resp.get('entity', [])relation_keywords = keyword_resp.get('relation', [])
假设 entity_keywords 为 [box, charger, phone],需要找出所有可能的源-目标(source-target)配对组合,以便对图进行全面查询:
pairs = list(combinations(entities, 2))
对于每个实体对,需要在图中查找所有节点和边:
paths = list(nx.all_simple_paths(G, source=u, target=target_nodes))
上述步骤(第1-6步,含以上代码)均已在以下函数中实现:
def search_kg2(G, query): response = get_llm_response(query, system_prompt_key_words) keyword_resp = json.loads(response) entity_keywords = keyword_resp.get('entity', []) relation_keywords = keyword_resp.get('relation', []) entities = [part.strip() for part in entity_keywords] pairs = list(combinations(entities, 2)) relations = [] for u, v in pairs: target_nodes = get_nodes(G, v) paths = list(nx.all_simple_paths(G, source=u, target=target_nodes)) for path in paths: for i inrange(len(path)-1): for key in G[path[i]][path[i+1]]: rel = G[path[i]][path[i+1]][key]['relation'] relations.append((path[i],rel, path[i+1])) for rel_keyword in relation_keywords: relations.extend([(u, rel, v) for u, v, rel in G.edges.data("relation") ifstr(rel) == rel_keyword]) return relations
当从上述函数获取到所有以三元组(entity->relation->entity)表示的边后,便可将这些三元组嵌入到指令式提示中,并传递给LLM:
context = f""" You are given facts from a knowledge graph: {triples} Answer the user query based ONLY on these facts. Answer in full sentence. Query: {query} """response = ollama.chat(model="gemma3:4b-it-qat", messages=[{"role": "user", "content": context}])print(f'query: {query}
Answer:{response["message"]["content"]}')
LLM将返回如下形式的答案:
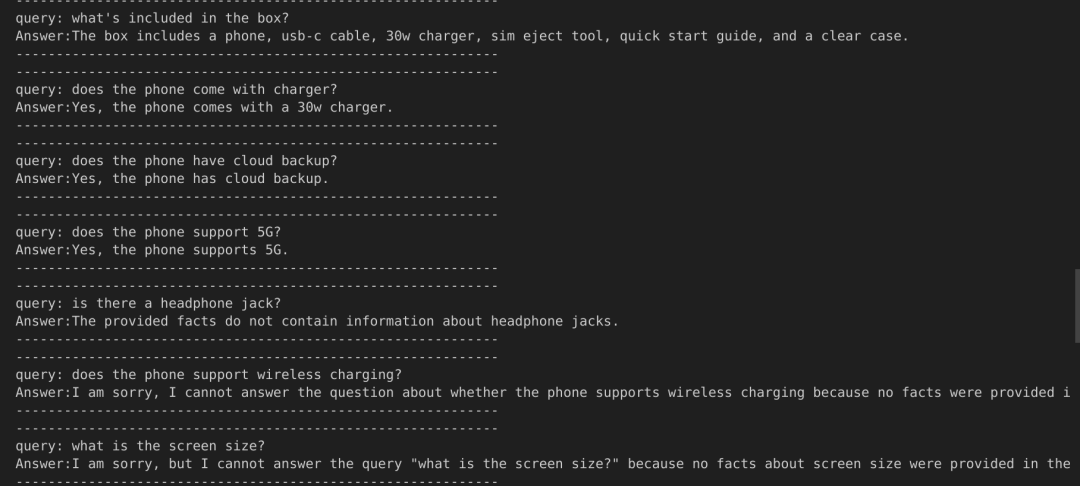
可见,对于缺乏相关数据或事实的问题,LLM会合理地拒绝作答。
本文所有代码可在以下GitHub链接中找到:
https://github.com/nayash/knowledge-graph-demo/blob/master/qa-from-kg.ipynb
系统局限性
尽管上述方法能够快速构建一个基础的问答系统,并大量利用LLM进行文本预处理和信息抽取,但仍存在一些不足。初步评估发现至少有以下几个问题:
系统无法回答“what is the warranty period?”这类问题。这是因为在知识图谱中,“warranty”被定义为关系标签,但LLM从问题中将其抽取为命名实体,导致系统无法找到对应的边。这表明用于构建知识图谱的核心系统提示词仍需进一步优化。
某些问题需要进行改写后系统才能回答。这类问题通常可归因于知识图谱的构建方式或从查询中提取的关键词。通过改进提示词可以修复这些问题。例如,当前使用的知识图谱中存在一条边:“phone → supportdualsim → nano sim”,这显然不够理想。然而,这些问题都可以通过更谨慎地设计用于构建知识图谱的提示词来纠正。如同在前一篇文章中提及,最初的提示词是基于ChatGPT生成并稍作修改的。在实际生产环境中,应投入更多时间打磨提示词。对于企业级应用,在资源允许的情况下,还可以尝试使用更大的模型。
总而言之,这种结合知识图谱与LLM的方法具有广阔前景,并且可以与检索增强生成(RAG)技术结合,进一步提升回答质量。